Skin Cancer Surgery Services: Comprehensive and Compassionate Care
Early Detection and Effective Treatment of Skin Cancer
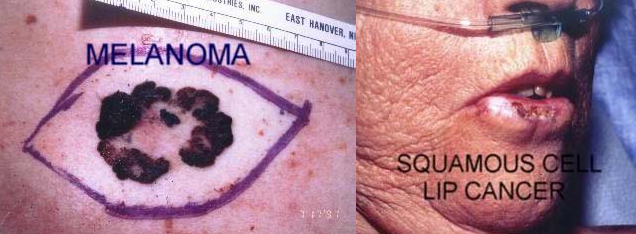
Skin cancer, the most common form of cancer in the United States, is largely curable when detected early. Dr. Weiss specializes in skin cancer surgery, addressing basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and malignant melanoma. Emphasizing the importance of early intervention, Dr. Weiss provides thorough exams and surgical removal of suspicious lesions to prevent growth and spread.
Understanding Skin Cancer and Its Causes
Comprehensive Approach to Skin Cancer Treatment
Ideal Candidates for Skin Cancer Surgery
The Importance of Prevention and Regular Check-Ups
What to Expect During Your Consultation
Surgery and Post-Operative Care
Choose Dr. Weiss for Expert Skin Cancer Surgery
Schedule your consultation with Dr. Weiss for comprehensive skin cancer treatment. With a focus on early detection, effective removal, and aesthetic restoration, Dr. Weiss is dedicated to providing personalized care for optimal health and confidence.
Skin cancer, the most common form of cancer in the United States, is largely curable when detected early. Dr. Weiss specializes in skin cancer surgery, addressing basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and malignant melanoma. Emphasizing the importance of early intervention, Dr. Weiss provides thorough exams and surgical removal of suspicious lesions to prevent growth and spread.
Understanding Skin Cancer and Its Causes
- Rising Incidence: An increasing number of cases each year due to factors like sun exposure and artificial tanning.
- Risk Factors: Fair skin, light-colored hair and eyes, numerous moles, family history, and outdoor lifestyle increase risks.
Comprehensive Approach to Skin Cancer Treatment
- Surgical Excision: Effective removal of cancerous lesions, often performed in outpatient settings under local anesthesia, with a focus on minimizing scarring and maximizing functional and aesthetic outcomes.
- Reconstructive Options: For more severe cases, reconstructive techniques, including scar revision and tissue transfer, restore appearance and function.
Ideal Candidates for Skin Cancer Surgery
- Broad Eligibility: Anyone with suspicious skin changes or diagnosed skin cancer. Early treatment is crucial for the best outcomes.
- Age and Health Considerations: Suitable for individuals of all ages, though certain health conditions may influence treatment plans.
The Importance of Prevention and Regular Check-Ups
- Preventative Measures: Protection from sun exposure, use of sunscreen, and wearing protective clothing are vital.
- Regular Skin Exams: Self-examinations and professional check-ups to catch any changes early, increasing the likelihood of successful treatment.
What to Expect During Your Consultation
- Personalized Evaluation: Dr. Weiss assesses each lesion and discusses treatment options, risks, recovery, and likely outcomes.
- Insurance and Coverage: While cosmetic procedures are typically not covered, reconstructive skin cancer surgery may be. Dr. Weiss's team assists with insurance inquiries.
Surgery and Post-Operative Care
- Anesthesia and Procedure: Tailored to the extent of cancer, focusing on complete removal and minimal scarring.
- Post-Surgery Follow-up: Regular visits to monitor for recurrence and manage any long-term skin health issues.
Choose Dr. Weiss for Expert Skin Cancer Surgery
Schedule your consultation with Dr. Weiss for comprehensive skin cancer treatment. With a focus on early detection, effective removal, and aesthetic restoration, Dr. Weiss is dedicated to providing personalized care for optimal health and confidence.