Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Hand Surgery: Advanced Techniques for Hand Restoration
Relief from Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) with Personalized Treatment
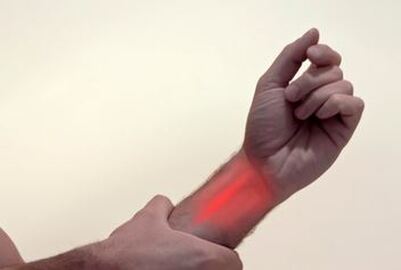
Living with the discomfort of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome? Dr. Weiss's approach combines non-surgical and surgical methods to provide relief from tingling, numbness, and impaired hand function.
Comprehensive Treatment for CTS
The Surgical Experience: Precision and Comfort
Expertise in Hand Surgery
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Choose Dr. Weiss for Expert Hand Surgery Services
Consider Dr. Weiss's comprehensive services for compassionate and expert solutions to hand health concerns, including Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and complex hand injuries. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and start your journey to improved hand function and comfort.
Living with the discomfort of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome? Dr. Weiss's approach combines non-surgical and surgical methods to provide relief from tingling, numbness, and impaired hand function.
Comprehensive Treatment for CTS
- Non-Surgical Options: Hand splints and anti-inflammatory medications are employed for effective symptom management.
- Surgical Intervention: When conservative measures are insufficient, minimally invasive surgery using the mini-incision microsurgery technique is recommended.
The Surgical Experience: Precision and Comfort
- Minimally Invasive Approach: A small incision near the wrist allows for precise nerve pressure release with minimal discomfort.
- Advanced Microsurgery: Utilizing state-of-the-art technology for effective treatment.
- Post-Surgery Care: Includes a long-acting block for a virtually pain-free initial 24 hours and a well-designed dressing and splint for recovery.
Expertise in Hand Surgery
- Treating a Spectrum of Hand Injuries: Our services address injuries to tendons, nerves, blood vessels, and more, using modern reconstructive techniques.
- Common Procedures: Include grafting, flap surgery, and replantation or transplantation, especially for severe injuries or amputations.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
- Patient-Centric Approach: Multiple operations and a period of hand therapy may be required, with an emphasis on patience and gradual recovery.
- Restoring Function and Feeling: Surgery and rehabilitation play a vital role in returning sensation and functionality to the hands.
Choose Dr. Weiss for Expert Hand Surgery Services
Consider Dr. Weiss's comprehensive services for compassionate and expert solutions to hand health concerns, including Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and complex hand injuries. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and start your journey to improved hand function and comfort.